|
SILVICS OF BEECH
(Fagus grandifolia Ehrh.)
Common names:
- American beech
Field identification aids:
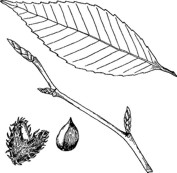
- beech retain their leaves through most of the fall and early winter
- buds are long with sharp ends
Average mature tree:
- 60 to 80 years old
- 12 m to 21 m (40' to 70') tall
- 20 cm to 60 cm (8" to 24") in diameter at breast height
Shade tolerance:
- very tolerant
Windfirmness:
- moderately windfirm
Rooting:
- shallow, wide spreading lateral roots
Reproduction:
- reproduces by seed, stump sprouting, or suckering from exposed roots
- tree may begin to produce seed when 40 years old, with full crop production after 60 years
- good seed crop produced every 2 to 3 years
- best seed germination occurs on moist humus or mineral soil
- poor seed germination on wet sites
Growing sites:
- range from moderately drained to well-drained
- best growth on well-drained loam sites
Associated species:
- red maple, sugar maple, yellow birch, red spruce, and hemlock on well drained sites
- rarely found in pure stands
Principal damaging agent:
- beech bark disease (insect-fungal partnership)
Notes:
- comprises 1.1% of merchantable volume of Nova Scotia forests
- a decrease in quality of beech due to heavy damage sustained by beech bark disease.
- used primarily for fuelwood
|