|
SILVICS OF WHITE ASH
(Fraxinus americana L.)
Common names:
- ash, American ash
Field identification aids:
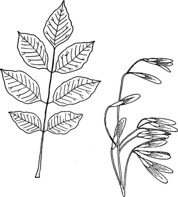
- compound leaves, with five to nine smooth, sparsely toothed leaflets
- tree is usually straight, with a cylindrical trunk
- buds are opposite (maples are the only other species with opposite buds)
- first set of lateral buds touch the terminal bud
Average mature tree:
- 60 to 80 years
- 18 m to 21 m (60' to 70') tall
- 45 cm to 75cm (18" to 30") in diameter at breast height
Maximum life span:
- 200 years
Shade tolerance:
- medium
- can withstand moderate shade in youth, but requires more sunlight as it matures
Rooting:
- wide-spreading lateral roots will grow deep if the soil conditions permit
Windfirmness:
- windfirm
Reproduction:
- reproduces by seed or stump sprouting
- tree may begin to produce seed when 20 to 30 years old, with good crop production after 40 to 50 years
- good seed crop production almost every year
- germination is best under full sunlight on a moist, mineral soil
Growing sites:
- range from moderately drained to well-drained
- grows best on deep, moist soils
Associated species:
- beech, white birch, yellow birch, sugar maple, and hemlock on well-drained sites
Principal damaging agents:
- anthracnose, forest tent caterpillar and ash rust causes distortion of leaves and tree form (alternate hosts of this rust are marsh and cord grasses)
Notes:
- white ash comprises 0.7% of the merchantable volume in Nova Scotia
- highly prized for its strong, shock resistant wood which makes excellent tool handles and sporting goods
|