|
SILVICS OF WHITE PINE
(Pinus strobus L.)
Common names:
- eastern white pine, soft pine, pattern pine, yellow pine, majestic pine
Field identification aids:
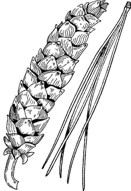
- only native five-needled pine
- needles are blue-green, long and soft to touch
- cigar shaped cones that are longer than those of other native pines
Average mature tree:
- 100 to 120 years old
- 24 m to 30 m (80' to 100') tall
- 601 cm to 90 cm (24" to 36") in diameter at breast height
Maximum life span:
- 200 - 450 years
Shade Tolerance:
- medium
Rooting:
- moderately deep, wide-spreading root system
- will produce a token tap root where soil permits
Windfirmness:
- moderately windfirm, more likely to break off than uproot
Reproduction:
- reproduces by seeding
- may produce seed as young as 20 with full crop production at 50 years
- good seed crop production every 3 to 5 years
- best germination occurs on exposed moist sandy loam
- litter is a poor seed bed for white pine
Growing sites:
- range from dry rocky sites to poorly drained sites
- best growth is on moist, loamy sands
Associated species:
- on poorly drained soils with black spruce and larch
- jack pine and red pine on dry sites
- hemlock, red spruce, yellow birch and sugar maple on well drained sites
Principal damaging agents:
- white pine blister rust, white pine weevil, redheaded pine sawfly, white-tailed deer
Notes:
- white pine comprises 8.3% of the merchantable volume in Nova Scotia
- many of the large trees standing above the rest in the forest are residual white pine
- the tallest and most stately of the eastern softwoods
- highly prized for interior finish
- straight grained, even textured, durable, light weight wood that takes nails, planing and painting well
|